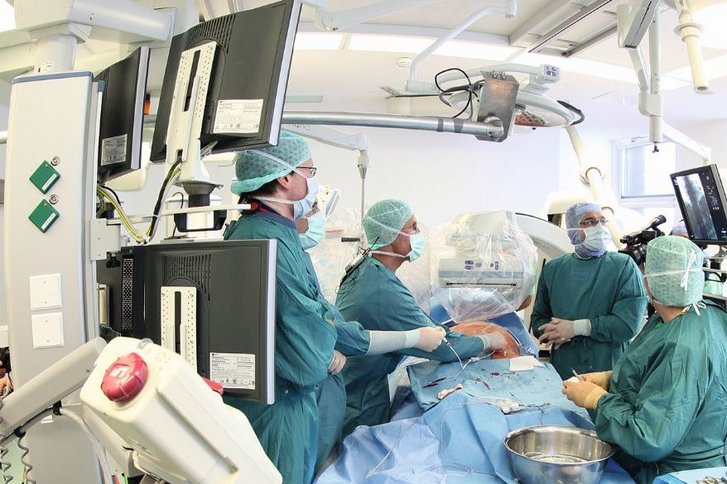
Balloon expansion, or dilatation as it is known in the medical world, is used to widen narrowed blood vessels. This method can be used when implanting a stent, for instance. It is recommended in particular in the case of narrowed, easily accessible coronary arteries. How is balloon dilation carried out, what are the risks, and what kind of aftercare is required? You can find out below..